ISO 9001 certification consultants in India, UAE, Saudi Arabia, Qatar, Oman, Kuwait, USA, Canada, Africa, Europe, UK and Middle East.
ISO 9001 consultants for ISO 9001 Certification, implementation and training. Quality Management System QMS Certification in India, Mumbai, Chennai, Hyderabad, Bangalore, Kolkata, Indore, Pune & Delhi.
ISO 9001 certification consultants in India, UAE, Saudi Arabia, Qatar, Oman, Kuwait, USA, Canada, Africa, Europe, UK and Middle East.

Lakshy Management Consultant Pvt. Ltd. is one of the largest and leading ISO 9001 consultants in India. We are transnational ISO certification consultants with clients in India, USA, UK, Saudi Arabia, Kuwait, Middle East, Europe, Africa, Australia, Singapore, Hong Kong, UAE, Qatar, Oman, Russia etc. We provide quick, result oriented and easy to implement consultation and training for ISO 9001 certificate.
We have been associated with organizations across the world for their ISO 9001 certification project. Whether you are a small organization or a multinational corporate, our proven consultation solutions will ensure that you implement ISO 9001 standard in the most effective manner with timely project completion.
ISO 9001 quality management system implementation with the consultants and experts of Lakshy Management Consultant Pvt. Ltd. not only assures 100% successful ISO 9001 certification but also improves process performance and business operations.
Consultants of our organization assist your company in your quality management context through ISO 9001 certification to get your company ISO 9001 certified quickly with the ease of implementation and in the most cost effective manner. We make sure that ISO 9001 standard implementation does not just become a documentation activity but also a way of life for the organization that lays a foundation for Total Quality Management and quality conscious organizational culture.
We offer onsite and online consultation solutions for ISO 9001 certification. Our customers have been utilizing our services not only for initial certification consultation but also for post certification consultation to ensure that we regularly add value to their business processes and quality standardization initiatives.
Our ISO 9001 certificate consultation services include awareness training, quality policy - objectives workshop, gap analysis, documentation design including manuals, procedures, work instructions, formats etc., implementation assistance & training, internal auditor training, lead auditor training, assistance in conducting internal audit, pre-assessment audit and everything required to ensure a 100% successful ISO 9001 certification audit within scheduled project completion time period.
Biggest benefit an organization gets out of ISO 9001 QMS is improvement in business process control through process standardization. No matter what benefits you are looking for from ISO 9001 certification, we will make sure that your organization benefits from ISO 9001 implementation and certification.
ISO 9001:2015 standard up gradation from ISO 9001:2008 version…..click to know how we can help your organization migrate to the newest ISO 9001 version quickly, easily and in the most effective manner.
ISO 9000 is a family of standards for quality management systems. ISO 9000 is maintained by ISO, the International Organization for Standardization and is administered by accreditation and certification bodies. Some of the requirements in ISO 9001 (which is one of the standards in the ISO 9000 family) include:-
A company or organization that has been independently audited and certified to be in conformance with ISO 9001 may publicly state that it is "ISO 9001 certified" or "ISO 9001 registered."
ISO 9000:2015, Quality management systems – Fundamentals and vocabulary. Covers the basics of what quality management systems are and also contains the core language of the ISO 9000 series of standards, and a guidance document, not used for certification purposes. This has been revised in year 2005.
ISO 9001:2015 , Quality management systems – Requirements. This is the most fundamental and important standard for all the organizations aiming to enhance process performance, service / product quality and enhance customer satisfaction.
ISO 9004:2009 Management for the sustained success of an organization - A quality management approach which talks about performance improvements and covers continual improvement. This gives you advice on what you could do to enhance a mature system. This standard very specifically states that it is not intended as a guide to implementation.
Note that the previous members of the ISO 9000 family, 9001, 9002 and 9003, have all been integrated into 9001. In most cases, an organization claiming to be "ISO 9000 registered" is referring to ISO 9001.
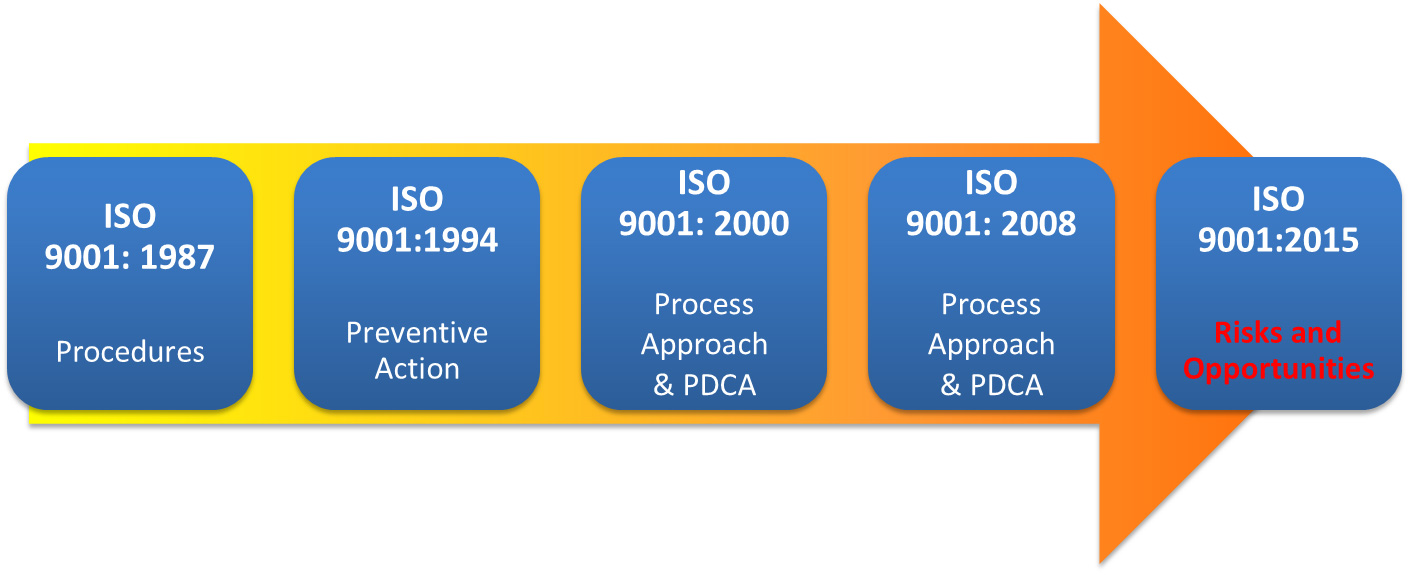
During WWII, there were quality problems in many British industries such as munitions, where bombs were exploding in factories during assembly. The adopted solution was to require factories to document their manufacturing procedures and to prove by record-keeping that the procedures were being followed. The name of the standard was BS 5750, and it was known as the management standard because it specified not only what to manufacture, but also how the manufacturing process was to be managed. According to Seddon, "In 1987, the British Government persuaded the International Organization for Standardization to adopt BS 5750 as an international standard. BS 5750 became ISO 9000."
ISO 9000:1987 had the same structure as the UK Standard BS 5750, with three 'models' for quality management systems, the selection of which was based on the scope of activities of the organization:
ISO 9001 : 1987 Model for quality assurance in design, development, production, installation, and servicing was for companies and organizations whose activities included the creation of new products.
ISO 9002 : 1987 Model for quality assurance in production, installation, and servicing had basically the same material as ISO 9001 but without covering the creation of new products.
ISO 9003 : 1987 Model for quality assurance in final inspection and test covered only the final inspection of finished product, with no concern for how the product was produced.
ISO 9000 : 1987 was also influenced by existing U.S. and other Defence Standards ("MIL SPECS"), and so was well-suited to manufacturing. The emphasis tended to be placed on conformance with procedures rather than the overall process of management — which was like the actual intent.
ISO 9000:1994 emphasized quality assurance via preventive actions, instead of just checking final product, and continued to require evidence of compliance with documented procedures. As with the first edition, the down-side was that companies tended to implement its requirements by creating shelf-loads of procedure manuals, and becoming burdened with an ISO bureaucracy. In some companies, adapting and improving processes could actually be impeded by the quality system.
ISO 9001:2000 combines the three standards 9001, 9002, and 9003 into one, now called 9001. Design and development procedures are required only if a company does, in fact, engage in the creation of new products. The 2000 version sought to make a radical change in thinking by actually placing the concept of process management front and center. ("Process management" was the monitoring and optimizing a company's tasks and activities, instead of just inspecting the final product). The 2000 version also demands involvement by upper executives, in order to integrate quality into the business system and avoid delegation of quality functions to junior administrators. Another goal is to improve effectiveness via process performance metrics — numerical measurement of the effectiveness of tasks and activities. Expectations of continual process improvement and tracking customer satisfaction were made explicit.
ISO 9001: 2008 introduces no new requirements. ISO 9001: 2008 only introduces clarifications to the existing requirements of ISO 9001: 2000 based on eight years of experience of implementing the standard worldwide with about one million certificates issued in 170 countries to date. It also introduces changes intended to improve consistency with ISO14001: 2004. The good news is that the 2008 release will not have the same impact. In fact, the ISO technical committee (TC176) which develops the ISO 9000 series of standards is purposely planning the next release as an amendment rather than a formal revision. The difference is that an "amendment" is focused on making changes for clarification purposes only and for better alignment with ISO 14001, the standard for environmental management. With the 2008 release, the committee is purposely intending not to introduce substantial changes that will affect the QMS processes and documentation of currently certified organizations. Thus, the new ISO 9001:2008 standard should have limited impact on companies already certified.
ISO does not itself certify organizations. Many countries have formed accreditation bodies to authorize certification bodies, which audit organizations applying for ISO 9001 compliance certification. Although commonly referred to as ISO 9000:2000 certifications, the actual standard to which an organization's quality management can be certified is ISO 9001:2000. Both the accreditation bodies and the certification bodies charge fees for their services. The various accreditation bodies have mutual agreements with each other to ensure that certificates issued by one of the Accredited Certification Bodies (CB) are accepted world-wide.
The applying organization is assessed based on an extensive sample of its sites, functions, products, services and processes; a list of problems ("action requests" or "non-compliances") is made known to the management. If there are no major problems on this list, the certification body will issue an ISO 9001 certificate for each geographical site it has visited, once it receives a satisfactory improvement plan from the management showing how any problems will be resolved.
An ISO certificate is not a once-and-for-all award, but must be renewed at regular intervals recommended by the certification body, usually around three years. In contrast to the Capability Maturity Model, there are no grades of competence within ISO 9001.
Two types of auditing are required to become registered to the standard: auditing by an external certification body (external audit) and audits by internal staff trained for this process (internal audits). The aim is a continual process of review and assessment, to verify that the system is working as it's supposed to, find out where it can improve and to correct or prevent problems identified. It is considered healthier for internal auditors to audit outside their usual management line, so as to bring a degree of independence to their judgments.
Under the 1994 standard, the auditing process could be adequately addressed by performing "compliance auditing":
The 2000 standard uses the process approach. While auditors perform similar functions, they are expected to go beyond mere auditing for rote "compliance" by focusing on risk, status and importance. This means they are expected to make more judgements on what is effective, rather than merely adhering to what is formally prescribed. The difference from the previous standard can be explained thus:
Under the 1994 version, the question that was asked was, "Are you doing what the manual says you should be doing?", whereas under the 2000 version, the question is, "Will this process help you achieve your stated objectives? Is it a good process or is there a way to do it better?”
The ISO 19011 standard for auditing applies to ISO 9001 besides other management systems like EMS (ISO 14001), FSMS (ISO 22000) etc.
The ISO 9001 standard is generalized and abstract. Its parts must be carefully interpreted, to make sense within a particular organization. Developing software is not like making cheese or offering counselling services; yet the ISO 9001 guidelines, because they are business management guidelines, can be applied to each of these. Diverse organizations—manufacturing companies, software development companies, trading organizations, service organizations, police departments, professional soccer teams and city councils —have successfully implemented ISO 9001:2000 systems.
Over time, various industry sectors have wanted to standardize their interpretations of the guidelines within their own marketplace. This is partly to ensure that their versions of ISO 9000 have their specific requirements, but also to try and ensure that more appropriately trained and experienced auditors are sent to assess them.
The TickIT guidelines are an interpretation of ISO 9000 produced by the UK Board of Trade to suit the processes of the information technology industry, especially software development.
AS 9000 is the Aerospace Basic Quality System Standard, an interpretation developed by major aerospace manufacturers. The current version is AS 9100.
PS 9000 is an application of the standard for Pharmaceutical Packaging Materials.
ISO/TS 16949 is an interpretation agreed upon by major automotive manufacturers (American and European manufacturers); the latest version is based on ISO 9001:2000. The emphasis on a process approach is stronger than in ISO9001:2000. ISO/TS 16949:2002 contains the full text of ISO 9001:2000 and automotive industry-specific requirements.
TL 9000 is the Telecom Quality Management and Measurement System Standard, an interpretation developed by the telecom consortium, Unlike ISO 9001 or the above sector standards, TL 9000 includes standardized product measurements that can be benchmarked.
ISO 13485:2003 is the medical industry's equivalent of ISO 9001:2008. While the standards it replaces were interpretations of how to apply ISO 9001 and ISO 9002 to medical devices, ISO 13485:2003 is a stand-alone standard. Compliance with ISO 13485 does not necessarily mean compliance with IS0 9001:2008.
It is widely acknowledged that proper quality management improves business, often having a positive effect on investment, market share, sales growth, sales margins, competitive advantage, and avoidance of litigation. The quality principles in ISO 9000:2000 are also sound, according to Wade, and Barnes, who say "ISO 9000 guidelines provide a comprehensive model for quality management systems that can make any company competitive." Barnes also cites a survey by Lloyd's Register Quality Assurance which indicated that ISO 9000 increased net profit, and another by Deloitte-Touche which reported that the costs of registration were recovered in as less as three months. According to the Providence Business News, implementing ISO often gives the following advantages:
In today's service-sector driven economy, more and more companies are using ISO 9000 as a business tool. Through the use of properly stated quality objectives, customer satisfaction surveys and a well-defined continual improvement program companies are using ISO 9000 processes to increase their efficiency and profitability.
With a team of highly qualified consultants and trainers having vast industrial experience, Lakshy Management Consultant Pvt. Ltd. assists organizations across the world to implement and achieve ISO 9001 certification. Our consultation approach is highly professional, time bound and effective resulting in the ease of implementation and adds value to the business processes of the client’s organization.
We offer ISO 9001 training, implementation, consultation, gap analysis, documentation, internal audits, preassessment audits, certification audit through best of the certification bodies and post certification enhancement / maintenance services to enable your organization to get the best out of ISO 9001 quality management system. Our services are globally accepted, authoritative and benchmarked in the field of ISO 9001 QMS:
Contact us at info@lakshy.com to get your organization ISO 9001 certified.
Upgrade from ISO 9001:2008 to ISO 9001:2015:-
Upgrade from ISO 14001:2004 to ISO 14001:2015:-
Upgrade from OHSAS 18001:2007 to ISO 45001:2018
Create a more efficient, effective operation
Increase customer satisfaction and retention
Reduce audits
Enhance marketing
Improve employee motivation, awareness, and morale
Promote international trade
Increases profit
Reduce waste and increases productivity















304, A-wing, 3rd floor, Shree Nand Dham, Sector 11, Opposite Raheja Arcade, CBD,Belapur, Navi Mumbai-400 614, India.